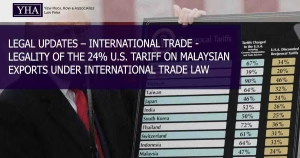
This legal update explores key provisions of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT 1947), focusing on Article I (Most-Favoured-Nation Treatment), Article II (Schedules of Concessions), Article XX (General Exceptions), and Article XXI (Security Exceptions). Article I mandates that any trade advantage granted by one contracting party to another must be extended unconditionally to all other parties. Article II ensures that imported goods from contracting parties receive treatment no less favourable than that outlined in agreed schedules, while also regulating permissible taxes and charges. Articles XX and XXI provide exceptions for measures necessary to protect public morals, health, security interests, and compliance with domestic laws. The provisions reflect the foundational principles of non-discrimination, transparency, and fair trade, while allowing for limited, well-defined exceptions. This summary is intended to provide a concise reference for businesses and legal practitioners involved in international trade law.